smartHeart - Biomechanical systems
with smart materials for application in fully implantable cardiac assist devices
Prof. Dr. Michael Wibmer, Prof. Dr. Markus Gitterle, M.Sc. Ludwig Wagmüller
Department Mechanical, Automotive and Aeronautical Engineering
Laboratory of Mathematics and Engineering Mechanics
Unlike conventional materials, smart materials react to external stimuli and change their properties accordingly. One example are electroactive polymers, which change their shape when stimulated with an electric field. Due to their high energy efficiency and possible large deformations, they offer a great potential to be used as actuators.
By controlling the external stimuli, it is possible to adjust the mechanical properties precisely. This means that the function of a component can be integrated into the structure itself. Thereby, a new scope in the field of product design is created, opening a wide field of application, from classic mechanical engineering to more specialized fields, like medical technology.
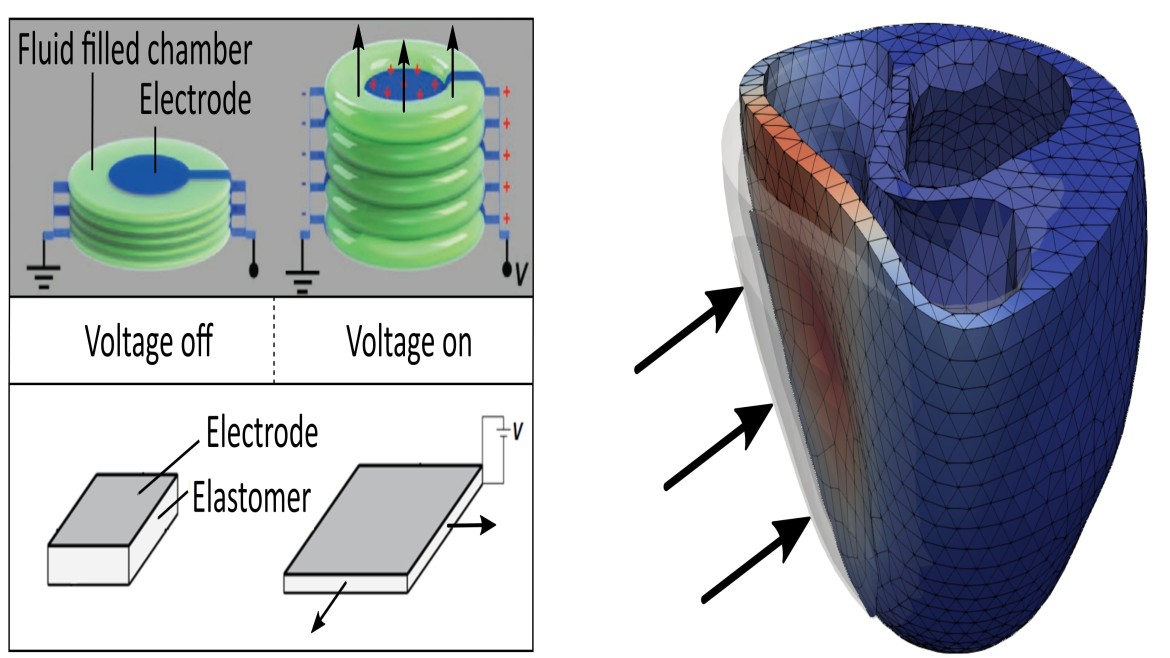
The objective of the project smartHeart is to evaluate actuators with intelligent materials for application to a cardiac support system. With the aid of modern numerical models, various actuator designs are simulated and optimized. As another possible example of such an intelligent actuator, the operating principle of a HASEL actuator is shown in the figure on top left.
To achieve these goals, a cooperation with the company AdjuCor GmbH has been started, since they develop innovative concepts and medical devices for minimally invasive and blood-contactless support for failing hearts. This cooperation offers the possibility to apply and verify the research results.
The use of smart materials in this application offers the potential for eliminating the need for a skin-crossing hydraulic or pneumatic supply line to an extracorporeal drive unit. This would alleviate the risk of infection and therefore, significantly improve the patient's quality of life.
Literature:
- [1] E. Acome et al., "Hydraulically amplified selfhealing electrostatic actuators with muscle-like performance", in Science 359.6371, pp. 61-65 (2018).
- [2] Z. Zhang et al., "New silicone dielectric elastomers with a high dielectric constant", in Modeling, Signal Processing, and Control for Smart Structures (2008).
Running duration:
01.02.2021 - 31.01.2024
Funded by:
Bavarian State Ministy of Science and the Arts
Project partner:
- AdjuCor GmbH
- Mechanics and High Performance Computing Group, Prof. Dr. Michael W. Gee, TUM